An Introduction to Search Engine Optimization

In this post, you’ll find:
- What is SEO?
- The 3 Pillars of Gaining Google’s Trust
- On-Page vs. Off-Page SEO
- 10 Tips for Improving Your SEO
Search engines have two main functions:
- crawling and indexing – they look at billions and billions of documents, webpages, files, videos, pictures, etc. on the internet and add them to their databases; and
- providing answers to their users – they use everything they’ve indexed to create lists of relevant websites to answer users’ questions.
Most web traffic comes from search engines (the biggest one being Google), so you want to make sure your website shows up on search engine results pages (SERPs). SEO helps you do that.
What is SEO?
Search engine optimization (SEO) is an important marketing tool for entrepreneurs and small business owners. It doesn’t have to cost a whole lot to implement, so you’ll be able to compete with larger companies.
SEO is the set of principles, methods, and techniques used to rank organically on those search engines. It helps you rank higher on SERPs, so you can get people to visit your website without having to purchase ad space.
Websites that show up on the front page of SERPs have a better chance of getting visitors.
You want your website to be one of the top search results because Google users tend to think that top ranking websites are the most trustworthy.
It can take a lot of time to get to that #1 spot on Google, so don’t expect to see results overnight with SEO.
The 3 Pillars of Gaining Google’s Trust
Google looks at over 200 factors when determining how to rank a website, but instead of worrying about each of those factors (which change frequently anyway), focus on these three main pillars to gain Google’s trust.
Indexed Age
Your website’s indexed age is not the date you first registered your domain name. It’s based on when Google first indexed (or found) your domain. If Google is just now finding you, they won’t trust you. They’ll scrutinize every little thing you do to make sure you’re not trying to trick them. If Google indexed your site a while ago and you haven’t done anything to make them doubt you, they’ll trust you a lot more.
Authority
Your website’s authority comes from how many people link back to your site. Now, you can’t just ask everyone you know to link back to your site. Google wants reputable sites with relevant content to link back to you.
If you’re regularly creating great content, other people will begin to share that content, so you’ll have a wide group of websites and social media profiles linking back to your site (then, your authority will grow).
Content
Content is king. Google really, really cares about the quality of your content. If you’re serious about using SEO to attract users to your website and grow your business, then you have to be serious about writing high-quality content that’s engaging, unique, and well-written.
Your website’s content should be keyword-centric (we’ll get to that later) and written for humans (not for search engines).
On-Page vs. Off-Page SEO
To take full advantage of SEO’s potential, you’ll need to engage in both on-page and off-page SEO.
Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO is largely out of your control, but definitely something you should pay attention to. It’s anything done to optimize your website that happens away from your actual website. Off-site SEO includes links from other websites and social media shares.
Link Building
Link building is getting other people and sites to link back to your content. There are three types of links to pay attention to – editorial, outreach, and self-created.
Editorial Links
Editorial links are links given naturally by other webpages just because they want to link to your company or content. You don’t have to do anything to get editorial links, besides creating great content.
Outreach Links
Outreach links require a little extra effort on your part. You get outreach links by contacting bloggers or reporters and submitting your site to online directories. You’ll usually have to explain why linking back to your website is in their best interest.
Self-Created Links
You should be careful with self-created links because they’re often considered “spammy”. If you pursue this strategy too aggressively, Google might penalize you, so you would see a drop in your rankings.
Self-created links can be part of your forum signatures, blog comments, and user profiles. Out of all the link building strategies, self-created links offer the lowest value. Although, they can still make an impact, if you use them sparingly.
On-Page SEO
On-page SEO is any optimization done to your website itself. It includes mobile-friendliness, keyword usage, title tags, meta descriptions, and more.
Keywords
Keywords are the words you want to rank for on the SERPs. It’s important to use keywords
- at least once in the title tag (as close to the beginning as possible);
- once prominently near the top of the page;
- at least 2 to 3 times in the body of your website (including variations, and if you have a lot of text, use it a few more times);
- at least once in the ALT attribute on any images on the page;
- once in the URL; and
- at least once in the meta description to encourage people to click on your site.
Keyword Research
Keyword research is one of the most important aspects of your SEO efforts. It helps you make sure you’re trying to rank for the right keywords (the ones that will attract your target market). You don’t just want to get visitors to your website, you want to get the right visitors to your website.
There are plenty of research tools out there to help you pick which keywords you want to rank for. You can use:
- Google AdWords Keyword Planner,
- Moz Keyword Explorer,
- Google Trends,
- Microsoft Bing Ads Intelligence, and
- Wordtracker’s Free Basic Keyword Demand.
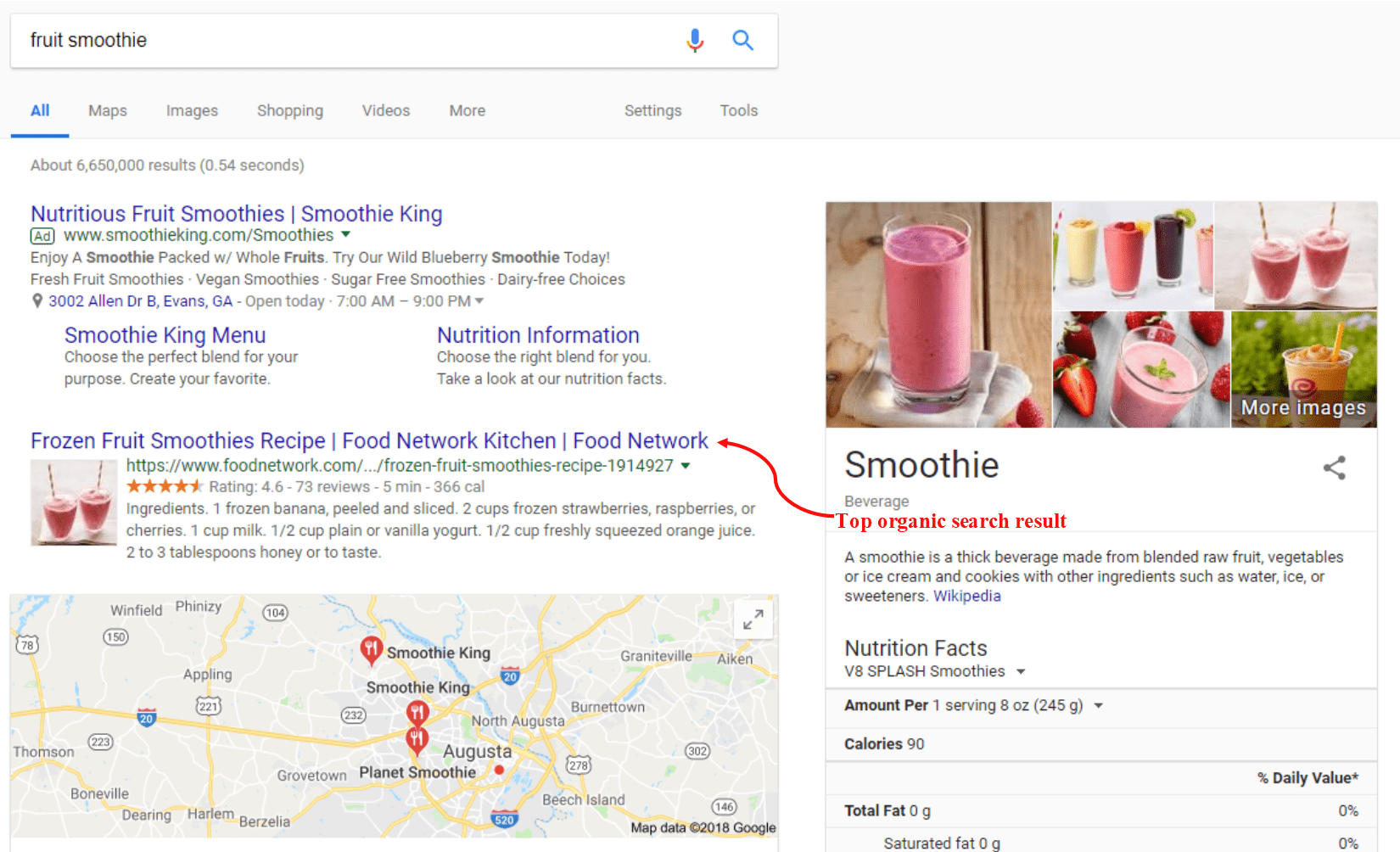
You should also pay close attention to long-tail keywords (often phrases, instead of words). Long-tail keywords often convert more visitors into readers or customers because they catch users later in the buying cycle. For example, if you sell fruit smoothies in the Augusta, Georgia area, you might try to rank for “fruit smoothies Augusta GA”, instead of just “fruit smoothies”.
When you’re doing keyword research, you want to try to find a keyword with little competition but a high volume of searches. Long-tail keywords are great for that.
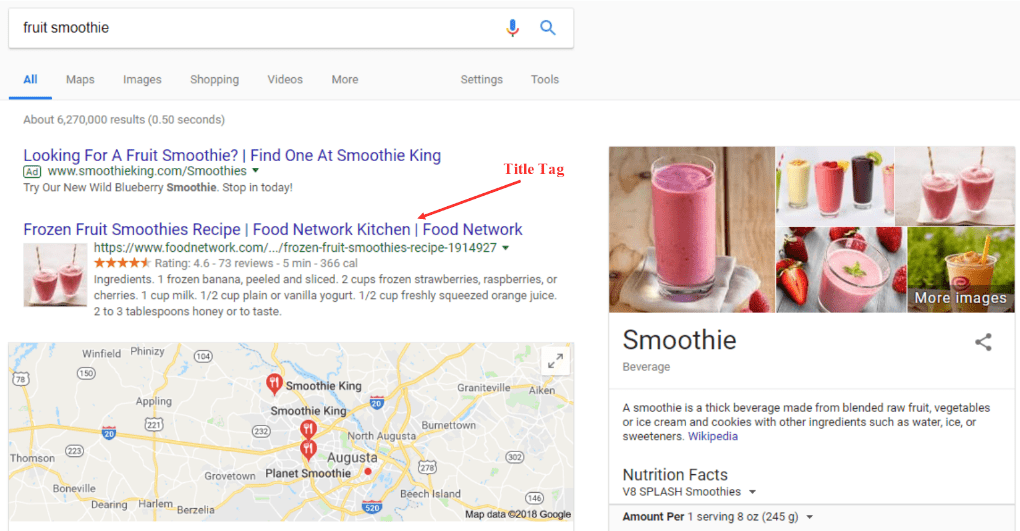
Title Tags
Title tags (<title>) are an HTML element that help Google know what to display as your title on the SERPs and are critical for user experience and SEO. It should be an accurate, concise description of your page’s content.
Use these tips to make the most of your title tags:
- Search engines generally only display the first 65-75 characters of a title tag, so keep it short.
- Place important keywords close to the front, so users are more likely to click it.
- End every title tag with a brand name mention to increase brand awareness and increase click through rates (CTR) for users who already like you.
- Make your title tags descriptive and readable, since they’re a new visitor’s first interaction with you.
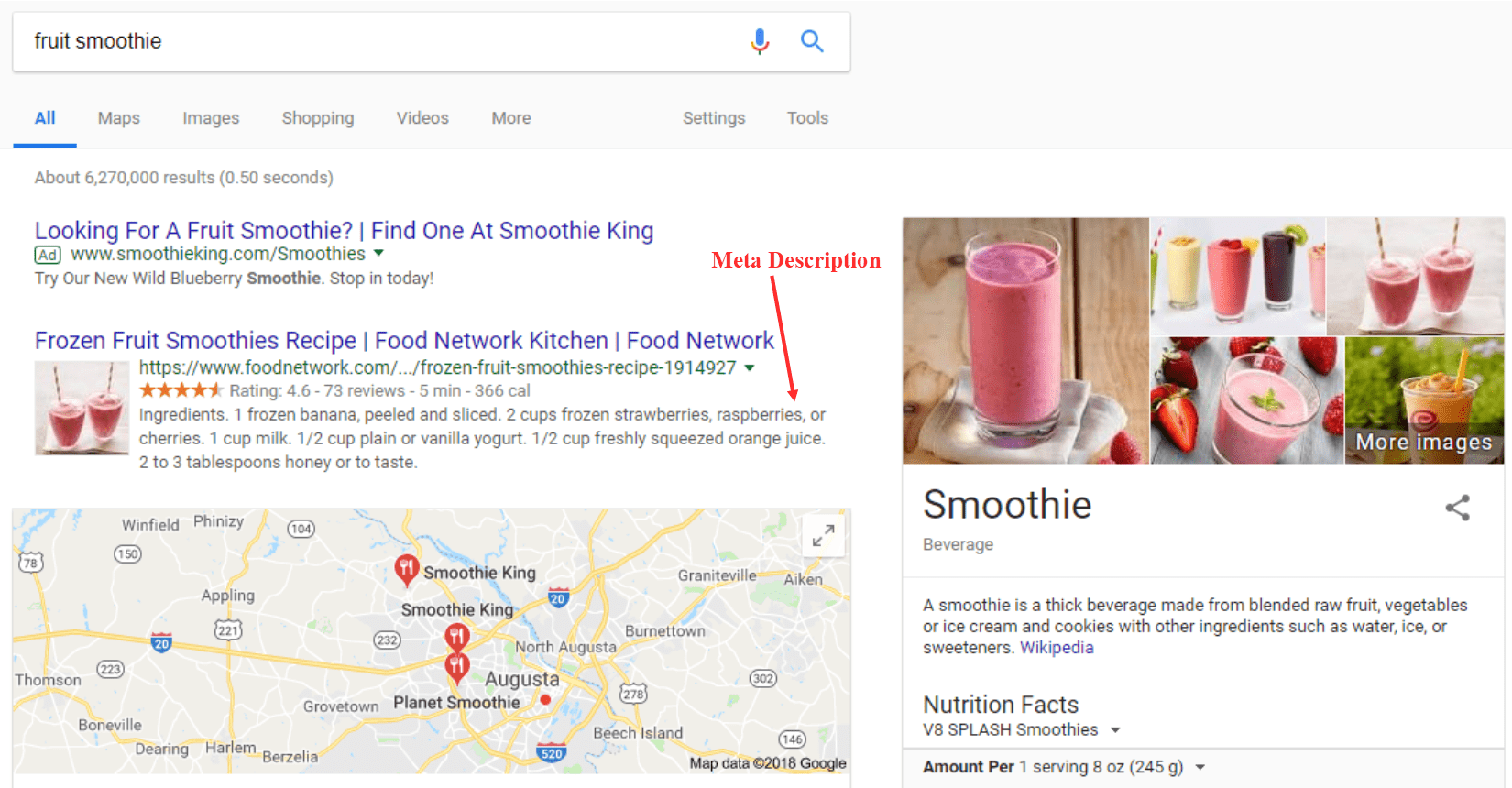
Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions are short description of your page’s content – basically, they’re like advertising copy.
Search engines don’t use your meta description to determine your SERP ranking, but they include it so users have an idea of what the website is about before they click. If you don’t include a meta description tag, then search engines will create a meta description for you (which probably won’t be as enticing as what you would create).
10 Tips for Improving Your SEO
As previously mentioned, SEO takes a lot of time, so you won’t see results overnight. Too many small business owners give up after a couple of months because they haven’t seen results yet. Don’t be one of them – hang in there and follow these tips:
1. Create Great Content
Have you noticed how often we’ve talked about content so far? That’s because great content is the cornerstone of any great SEO strategy. Without great content, you’ll have a hard time getting to the first page of the SERPs.
Try to create content that engages your site’s visitors. The more engaging your content is, the more your readers will want to share your content, so the higher you’ll be ranked by search engines.
Your content should help your readers solve a problem, teach them something, or answer their questions. (FAQs make great content!)
You can make the content as long or short as you like, but long-form content (1,000+ words, like what you’re reading right now) seems to do the best because it answers every question a user could have.
No matter what kind of content you create, make sure you’re writing it for humans to read, not for search engines.
2. Don’t Try to Rank for Everything
When you’re doing keyword research, pay attention to the keywords that can have the most impact and mean the most to your company. Don’t try to rank for every single keyword. If you try to rank for everything, you’ll be tempted to keyword stuff (cramming keywords into your content, even though it doesn’t make any sense), which Google really frowns on. Instead, use your keywords naturally and strategically.
3. Increase Engagement
Google pays a lot of attention to how long people stay on your webpage. If someone clicks on your website, then leaves after a few seconds without clicking on anything else, Google thinks you didn’t answer their question.
So, find new and interesting ways to increase your readers’ engagement. You can add videos, audio, podcasts, polls, and quizzes to encourage people to stick around for a while.
4. Add Relevant Outbound Links
I just told you to add content that encourages people to stay on your site longer, and now I’m telling you to add links to other people’s websites – that sounds crazy, right?
When you link to other sites that further answer someone’s question, you’re helping them continue their educational journey. They’ll remember that you wanted to help them anyway you could, even if you didn’t have all the answers, so they’ll trust you and keep coming back for more.
Google also really likes to see outbound links. But, remember that quality always trumps quantity, so don’t worry about stuffing your content with links to other sites. Only link to trusted sites with content related to what you’re creating.
5. Create a Great User Experience
Creating a great user experience is as important as creating great content. If you have great content, but users can’t navigate your site, or if your site loads too slowly, they’ll never give your content a chance.
Try to optimize your site to load quickly and look just as good on a phone as it does on a computer.
Categorize your content so users can quickly find related content, and it’s usually a good idea to include a search bar.
6. Pay Attention to Your Internal Links
Linking to other parts of your website helps search engines reach every page of your website. You want to make sure that search engines can get to any of your pages, so make sure you link to each page at least once from somewhere else on your website.
7. Limit Your Ad Usage
Nobody likes ads – it’s why adblockers have become so popular. But, people really don’t like seeing tons of ads as soon as they get to your website.
If people only see ads when they first get to your website, they won’t have a good user experience and will probably leave pretty quickly. They’ll also slow down your website, making the user experience even worse.
8. Don’t Even Think About Being Sneaky
Black hat SEO involves taking shortcuts (like keyword stuffing) to try to exploit SEO tactics. But, Google will catch you, and your strategies will backfire, as you move further and further down the SERPs into oblivion.
If you’re thinking about hiring someone to do SEO and they promise you’ll be on the first page of Google next week, run as fast as you can. If they’re making those promises, they’re probably using some sort of black hat SEO.
Instead of trying to take shortcuts, focus on adding value. If you add value, your rankings will improve over time.
9. Follow Google’s Webmaster Guidelines
Google doesn’t want to hide all their tactics from you, so they put out their Webmaster Guidelines. These guidelines offer tips for making your website search engine friendly.
Some of the tips include:
- Make your pages primarily for users, not search engines.
- Don’t deceive your users.
- Avoid cloaking (where your page looks different to users than it does to search engines).
- Provide fresh content regularly.
10. Measure Your Results
Like every other marketing strategy, you should always measure your SEO results and progress. If you don’t measure your results, you won’t know how well you’re doing or if your efforts are making a difference.
The most common (and free!) tool for measuring your SEO efforts is Google Analytics. By monitoring your webpage’s traffic and which keywords are helping the most, you’ll be able to adjust your strategy for even better results.
Conclusion
Search engine optimization is complex and complicated, but an important part of any online marketing strategy. By creating user-friendly websites with great content, you’ll be able to gain the trust of Google and other search engines. After you’ve gained their trust, they’ll reward you by putting your webpages higher up on users’ search results, so you’ll gain more visitors. And, more visitors mean more customers.